Understanding Sustainable Homes
Sustainable homes prioritize reducing environmental impact without compromising comfort or functionality. These properties integrate eco-conscious designs and technologies to ensure long-term resource efficiency.
What Are Sustainable Homes?
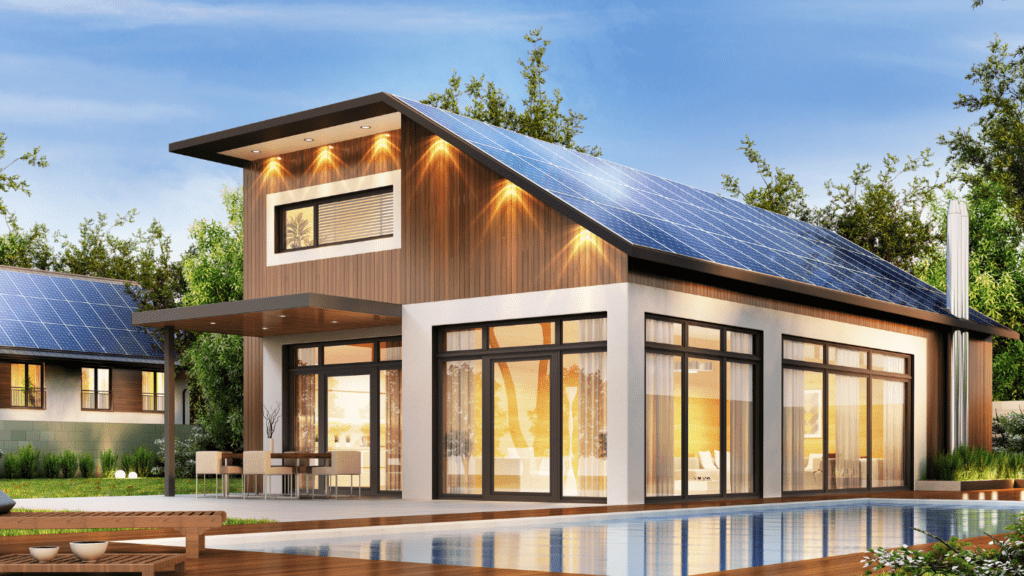
Sustainable homes are residential buildings designed with practices that minimize harm to the environment. They incorporate energy-efficient systems, renewable energy sources like solar or wind power, and low-impact construction materials. These homes emphasize conserving natural resources while enhancing indoor living quality.
For instance, many sustainable homes rely on high-performance insulation, energy recovery ventilation systems, and reclaimed building materials. The goal is to optimize energy use, reduce waste, and lower the carbon footprint during construction and daily operations.
- Energy Efficiency: Features like LED lighting, energy-efficient appliances, and double-glazed windows enhance energy conservation.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Solar panels, geothermal systems, or wind turbines generate clean energy on-site.
- Water Conservation: Installing rainwater harvesting systems, low-flow fixtures, and graywater recycling reduces water usage.
- Sustainable Materials: Reclaimed wood, bamboo, and recycled metals are used in construction to limit reliance on unsustainable resources.
- Indoor Air Quality: Ventilation systems, non-toxic paints, and low-VOC materials ensure healthier indoor environments.
- Smart Technologies: Smart thermostats and automated energy management tools optimize resource usage.
By combining these features, sustainable homes balance environmental responsibility with modern living. They address growing environmental concerns in the housing market.
The Rise of Sustainable Homes in Real Estate

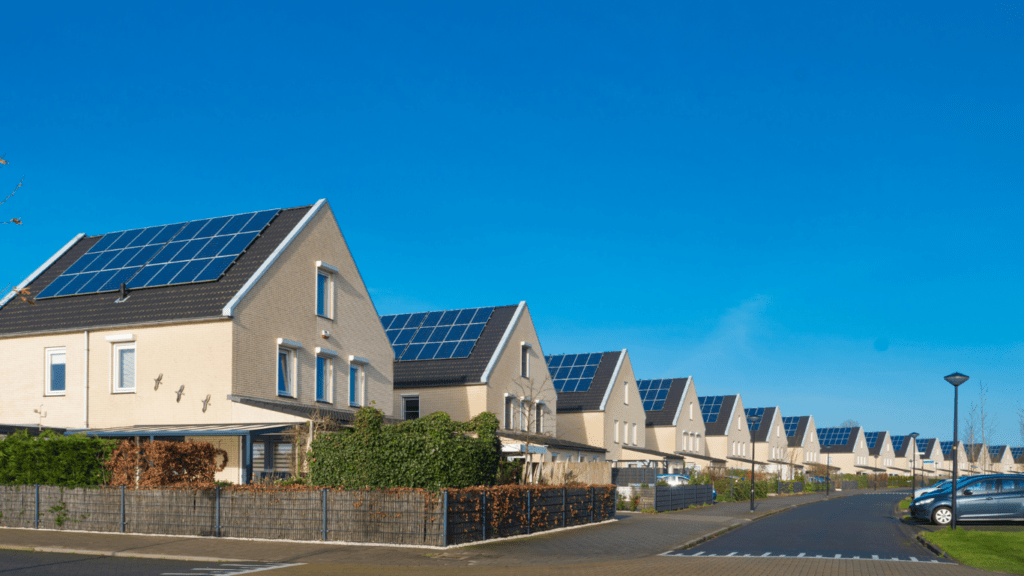
Demand for sustainable homes in real estate continues to grow as environmental awareness and resource conservation take priority. Developers and buyers alike are driving the transformation of housing markets to meet sustainability goals.
Market Trends Driving the Popularity
Increased consumer demand, governmental incentives, and industry innovation contribute to the rise of sustainable homes. Real estate buyers increasingly prioritize green certifications like LEED and ENERGY STAR when choosing properties. Features like renewable energy systems and net-zero energy designs are highly sought after.
Regulatory changes also propel sustainable construction. In many regions, building codes now encourage energy-efficient designs, while grants and tax benefits incentivize renewable energy installation. Shifts in market preferences, driven by younger generations, further amplify interest in eco-conscious properties.
Data from the National Association of Realtors shows that 68% of buyers consider energy-efficient features important. This indicates a clear shift in consumer behavior and underscores the growing relevance of sustainability in residential real estate.
Environmental and Economic Benefits
Sustainable homes reduce environmental impact by lowering energy consumption and minimizing waste, enabling a smaller carbon footprint. Features like:
- solar panels
- rainwater harvesting systems
- efficient HVAC units
help decrease reliance on finite resources. These homes also deliver significant economic advantages. Energy-efficient appliances and renewable energy installations save homeowners on utility costs. On average, homes with solar arrays reduce annual electricity expenses by $1,000 to $1,500, according to the U.S. Department of Energy. Additionally, green housing often commands higher resale values compared to traditional properties.
Reduction in maintenance costs adds another layer of appeal. Using durable materials like reclaimed wood and recycled metal ensures long-term sustainability while decreasing repair expenses. Sustainable homes represent both an environmentally conscious choice and a sound financial investment.
Technologies and Innovations in Sustainable Living
The real estate market is adopting advanced technologies to make homes more sustainable. These innovations focus on enhancing energy efficiency, resource management, and automation to cater to environmentally aware buyers.
Renewable Energy Systems
Renewable energy systems play a crucial role in reducing carbon footprints. Solar panels, for example, convert sunlight into electricity to power homes while lowering energy bills. Wind turbines and geothermal heat pumps offer additional renewable options, particularly in areas with suitable climates. Battery storage systems improve energy reliability by storing excess power for later use, ensuring efficient energy utilization.
Efficient Water Management
Water management systems enhance resource conservation in sustainable homes. Rainwater harvesting systems collect and store rainwater for non-potable uses, such as irrigation and flushing. Low-flow fixtures, including faucets and showerheads, reduce water usage without compromising functionality. Greywater recycling systems treat wastewater from sinks and showers, making it reusable for landscaping or other purposes.
Smart Home Integration
Smart home technology optimizes energy and resource use in real-time. Smart thermostats adjust heating and cooling settings based on occupancy patterns, minimizing energy waste. IoT-enabled devices, such as smart lighting and energy monitors, allow for remote control and better consumption tracking. Home automation systems integrate with renewable energy setups, ensuring maximum efficiency while enhancing convenience.
Challenges in Adopting Sustainable Homes
Adopting sustainable homes involves addressing several obstacles despite their numerous benefits. Cost considerations and limited awareness remain the primary barriers hindering widespread adoption.
Cost Barriers
Sustainable homes often require higher initial investments compared to traditional housing. Features like solar panels, energy-efficient appliances, and smart technologies can increase upfront costs by 10-20%, as per the U.S. Department of Energy. Additionally, sourcing green materials like reclaimed wood or low-impact cement can be expensive. Financing these investments may be challenging for first-time buyers or low-income families, even with incentives like federal tax credits or state-specific subsidies.
Awareness and Education
Limited understanding of sustainable housing features impedes adoption rates. Many buyers are unaware of their long-term economic benefits, such as energy savings or increased resale value. A 2023 survey by the NAHB revealed that 42% of prospective homeowners couldn’t identify eco-friendly certifications like LEED or ENERGY STAR. Builders and real estate agents often lack sufficient educational resources to guide consumers. Enhanced outreach and training programs could bridge this knowledge gap in various market segments.